Hair is more than a cosmetic feature. It is closely linked to identity, confidence, health, and overall well-being. As concerns about hair loss, hair shedding, and scalp problems increase worldwide, many people find themselves asking an important question: What is a trichologist?
A trichologist is a specialist who focuses on the science of hair and scalp health. While they are not medical doctors in the traditional sense, trichologists play a critical role in identifying, managing, and supporting treatment plans for a wide range of hair and scalp conditions.
This article provides a complete, in-depth explanation of the meaning of a trichologist, their role, what they can and cannot do, and how they help with hair loss, including modern approaches such as hair restoration, platelet rich plasma PRP, and collaboration with medical professionals in hair transplantation.
The word trichology comes from the Greek word “trikhos”, meaning hair.
A trichologist is a trained specialist who studies:
Trichologists focus on diagnosing functional and structural problems of the hair and scalp, identifying contributing lifestyle, nutritional, hormonal, and environmental factors.
They are often the first professionals people consult when they experience unexplained hair shedding or changes in hair quality.
This is one of the most common questions.
👉 No, a trichologist is not a medical doctor.
However, this does not reduce their importance.
That said, experienced trichologists are highly skilled at:
In many cases, trichologists work alongside doctors, especially in advanced hair restoration clinics.
The primary role of a trichologist is to diagnose and treat hair and scalp problems non-surgically.
Their responsibilities include:
A trichologist’s approach is holistic, meaning they look beyond the scalp to understand why hair loss is occurring.
A professional trichologist typically begins with a detailed consultation.
They then perform a scalp examination using tools such as:
This allows close inspection of hair follicles, scalp health, and signs of inflammation, miniaturization, or breakage.
Trichologists are trained to recognize and manage many types of hair loss, including:
Androgenetic Alopecia
Also known as male or female pattern hair loss, androgenetic alopecia is the most common cause of hair thinning.
A trichologist can:
Telogen effluvium is characterized by sudden, diffuse hair shedding.
Common triggers include:
Trichologists play a major role in identifying triggers and supporting recovery by restoring the normal hair growth cycle.
Female pattern hair loss often presents differently than male hair loss.
Trichologists help by:
A trichologist does not focus only on hair loss. They also manage many hair and scalp conditions, such as:
These issues can indirectly affect hair growth and overall hair quality if left untreated.
In most countries, trichologists cannot prescribe medications.
However:
For example, a trichologist may recommend discussing certain treatments with a dermatologist, especially when dealing with androgenetic alopecia or underlying medical conditions.
Trichologists focus on evidence-based, non-surgical treatment options.
These may include:
Their goal is to optimize the scalp environment and support healthy hair follicles.
Platelet rich plasma PRP has become an important part of modern hair care.
While PRP is a medical procedure, trichologists often:
PRP works by stimulating hair growth through growth factors that support follicle activity.
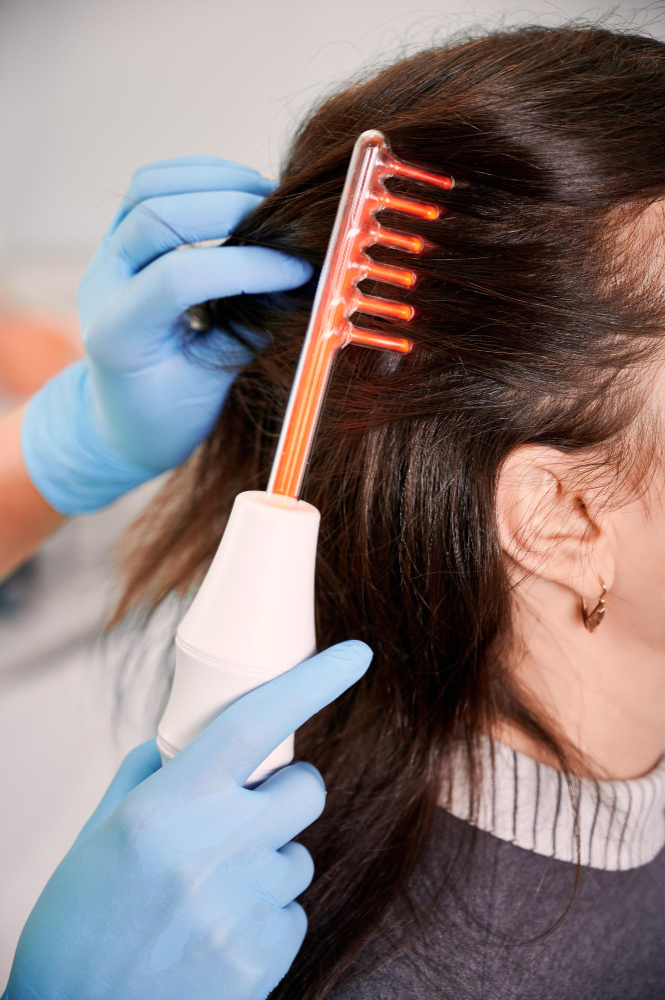
In many advanced clinics, trichologists are an integral part of hair restoration teams.
They:
This collaborative model improves outcomes and patient satisfaction.
A trichologist does not perform hair transplantation, but their role is still critical.
Before surgery:
After surgery:
This makes them valuable allies in surgical hair restoration journeys.
Professional credibility matters.
Reputable trichologists often train through recognized institutions such as the World Trichology Society or similar organizations.
These bodies:
Patients should always verify training and credentials.
When people ask how trichologists treat hair loss, the answer lies in personalization.
They consider:
Rather than offering a one-size-fits-all solution, trichologists build long-term strategies to support sustainable hair growth.
Trichologists also educate patients about potential side effects of treatments, including:
This guidance helps patients make informed decisions and avoid unnecessary risks.
You should consider seeing a trichologist if you experience:
Early consultation often leads to better outcomes.
| Trichologist | Dermatologist |
| Hair and scalp specialist | Medical skin doctor |
| Holistic hair focus | Medical diagnosis |
| Non-surgical care | Prescribes medication |
| Long-term monitoring | Treats diseases |
They often work best together, not in competition.
As awareness grows, trichology continues to evolve.
Trichologists are increasingly involved in:
Their role in helping people understand and manage hair health will only expand.
So, what is a trichologist?
A trichologist is a specialized professional dedicated to understanding and managing hair and scalp health. They bridge the gap between cosmetic care and medical treatment, offering personalized, science-based support for a wide range of types of hair loss and scalp conditions.
While they do not replace doctors, they are essential partners in modern hair growth, hair restoration, and long-term hair care strategies.
For anyone concerned about hair health, a trichologist can be a powerful first step toward clarity, confidence, and informed treatment choices.
One of the most valuable contributions of a trichologist is their ability to diagnose and treat hair loss accurately at an early stage. Hair loss is rarely random; it usually follows identifiable biological or environmental patterns.
A trichologist evaluates:
By analyzing these factors together, they can distinguish between shedding-related conditions and progressive disorders such as androgenetic alopecia.
Hair loss is not a single condition. Trichologists are trained to recognize multiple types of hair loss, each requiring a different approach.
This genetically driven condition affects both men and women and is the most common cause of hair thinning worldwide. Trichologists focus on:
Telogen effluvium causes sudden and excessive hair shedding, often triggered by stress, illness, surgery, or hormonal shifts. Trichologists identify triggers and help reset the hair growth cycle.
Female pattern hair loss is often diffuse and emotionally distressing. Trichologists help differentiate it from nutritional deficiencies and autoimmune conditions, ensuring proper treatment options are chosen.
Healthy hair follicles depend on a healthy scalp environment. Trichologists pay close attention to:
Poor scalp health can weaken follicles, disrupt hair growth, and increase hair shedding, even in individuals without genetic hair loss.
A trichologist’s primary goal is to optimize hair growth, not just stop hair loss.
They work to:
By improving these parameters, patients often notice thicker, stronger hair even before regrowth becomes visible.
Yes. In fact, most trichologists specialize in non-surgical hair restoration.
They may use:
Surgery is not always necessary, especially in early-stage hair loss or temporary shedding conditions.
Platelet rich plasma PRP has become a cornerstone of modern hair restoration strategies.
Although PRP is a medical procedure, trichologists:
PRP can improve follicle signaling and support dormant follicles returning to active hair growth.
Trichologists play an important role in patient safety by educating clients about side effects.
Common side effects discussed include:
By anticipating and managing side effects early, trichologists help patients stay consistent with treatment plans.
Many medical conditions influence hair quality and density.
Trichologists are trained to recognize warning signs of:
While they do not diagnose diseases, they know when referral to a medical doctor is essential.
Understanding the difference between a trichologist and a hair transplant surgeon is crucial.
A trichologist:
A surgeon:
The best outcomes occur when both professionals collaborate.
Not all hair loss can be managed conservatively. In advanced cases, hair transplantation may be recommended.
Trichologists help by:
This teamwork improves graft survival and long-term results.
Hair loss affects more than appearance—it affects identity and confidence.
Trichologists provide:
This emotional component is often overlooked but plays a major role in treatment success.
Membership or training through organizations such as the World Trichology Society indicates a commitment to ethical practice and evidence-based care.
Patients should always:
Professional standards protect both patients and practitioners.
True hair restoration is a long-term process.
Trichologists help design strategies that:
This long-term vision is one of the greatest strengths of trichology.
Seeing a trichologist early can:
Early intervention is often the difference between stabilization and progression.
A trichologist is far more than a “hair consultant.” They are trained specialists who understand the complex interaction between hair follicles, scalp health, biology, and lifestyle.
They help:
In modern hair care, trichologists are indispensable allies—bridging science, care, and long-term results.